Inhaltsverzeichnis
assoc_legendre()
#include <cmath>
double assoc_legendre(unsigned n, unsigned m, double x) // C++17
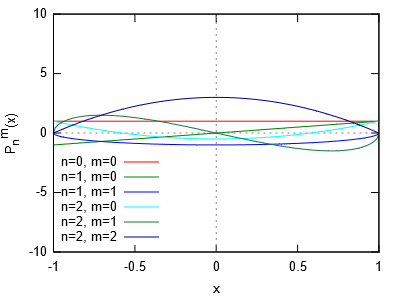 Liefert Wert für das zugeordnete Legendre-Polynom
(genauer: die zugeordnete Kugelfunktion)
$P_n^m(x) = (-1)^m (1-x^2)^{m/2}\frac{d^m}{dx^m} P_n(x)$ mit $0 \leq m \leq n$ und $|x| \leq 1$.
Liefert Wert für das zugeordnete Legendre-Polynom
(genauer: die zugeordnete Kugelfunktion)
$P_n^m(x) = (-1)^m (1-x^2)^{m/2}\frac{d^m}{dx^m} P_n(x)$ mit $0 \leq m \leq n$ und $|x| \leq 1$.
Parameter
n | Grad des Grundpolynoms |
m | Grad der Ableitung |
x | reell, $|x| \leq 1$ |
Ergebnis
Rückgabewert: $P_n^m(x)$
Siehe auch
Beispiel
- assoc_legendre.cpp
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> int main() { std::cout << "# x n=0,m=0 n=1,m=0 n=1,m=1 n=2,m=0 n=2,m=1 n=2,m=2\n"; for (int i = -100; i <= 100; ++i) { double x = 0.01*i; std::cout << x << '\t' << std::assoc_legendre(0, 0, x) << '\t' << std::assoc_legendre(1, 0, x) << '\t' << std::assoc_legendre(1, 1, x) << '\t' << std::assoc_legendre(2, 0, x) << '\t' << std::assoc_legendre(2, 1, x) << '\t' << std::assoc_legendre(2, 2, x) << '\n'; } }