kennen:lib:ellint_3
Inhaltsverzeichnis
ellint_3()
#include <cmath>
double ellint_3(double k, double nu, double phi) // C++17
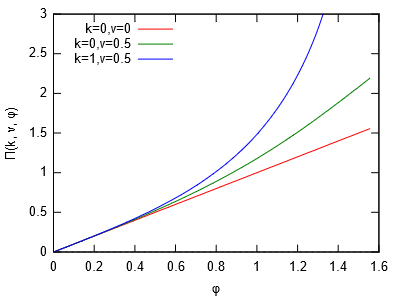 Liefert Wert des unvollständigen Elliptischen Integrals 3. Art
$\Pi(k,\nu,\varphi) = \int_0^\varphi \frac{d\theta}{(1-\nu \sin^2 \theta)\sqrt{1-k^2 \sin^2 \theta}}$
für $|k| \leq 1$ und $\nu > -1/\sin^2 \theta$.
Liefert Wert des unvollständigen Elliptischen Integrals 3. Art
$\Pi(k,\nu,\varphi) = \int_0^\varphi \frac{d\theta}{(1-\nu \sin^2 \theta)\sqrt{1-k^2 \sin^2 \theta}}$
für $|k| \leq 1$ und $\nu > -1/\sin^2 \theta$.
Parameter
k | Modul $|k| \leq 1$ |
nu | Charakteristik |
phi | Amplitude |
Ergebnis
Rückgabewert: $\Pi(k,\nu,\varphi)$.
Siehe auch
Beispiel
- ellint_3.cpp
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> int main() { const auto pi = std::acos(-1.0); std::cout << "# k=0,n=0 k=0,n=0.5 k=1,n=0.5\n"; for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) { double phi = 0.01*i*pi/2; std::cout << phi << '\t' << std::ellint_3(0.0, 0.0, phi) << '\t' << std::ellint_3(0, 0.5, phi) << '\t' << std::ellint_3(1, 0.5, phi) << '\n'; } }
Anmerkung: Die gcc-Bibliothek verwendete bis gcc 7.2.0 das entgegengesetzte Vorzeichen für die Charakteristik $\nu$ (GCC bug report 66689). Ab gcc 8.0.0 HEAD 201711 scheint dies behoben (C++2a, Wandbox):
- ellint3_test.cpp
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> int main() { const auto pi = std::acos(-1.0); const auto k = 0.0; std::cout << "nu\tincomp.\tcompl.\texpect\n"; for (auto nu : {-0.9, -0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 0.9}) { auto expected = pi/(2*std::sqrt(1-nu)); std::cout << nu << '\t' << std::ellint_3(k, nu, pi/2) << '\t' << std::comp_ellint_3(k, nu) << '\t' << expected << '\n'; } }
kennen/lib/ellint_3.txt · Zuletzt geändert: von 127.0.0.1
